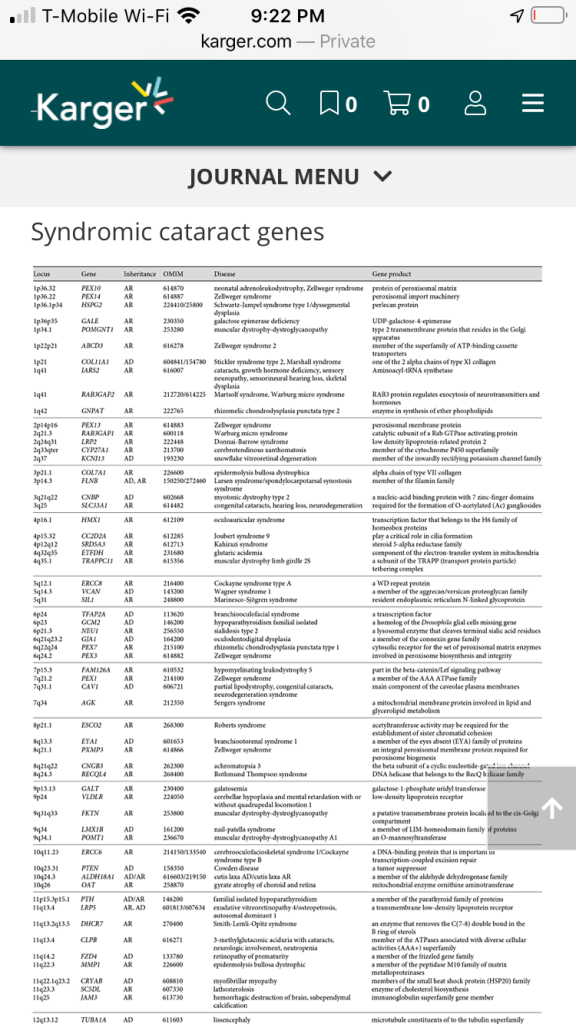
Table 1
Syndromic cataract genes
| Gene | Inheritance | Disease | Gene product |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEX10 | AR | neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, Zellweger syndrome | protein of peroxisomal matrix |
| PEX14 | AR | Zellweger syndrome | peroxisomal import machinery |
| HSPG2 | AR | Schwartz-Jampel syndrome type 1/dyssegmental dysplasia | perlecan protein |
| GALE | AR | galactose epimerase deficiency | UDP-galactose-4-epimerase |
| POMGNT1 | AR | muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy | type 2 transmembrane protein that resides in the Golgi apparatus |
| ABCD3 | AR | Zellweger syndrome 2 | member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette transporters |
| COL11A1 | AD | Stickler syndrome type 2, Marshall syndrome cataracts, growth hormone deficiency, sensory neuropathy, sensorineural hearing loss, skeletal dysplasia | one of the 2 alpha chains of type XI collagen |
| IARS2 | AR | Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase | |
| RAB3GAP2 | AR | Martsolf syndrome, Warburg micro syndrome | RAB3 protein regulates exocytosis of neurotransmitters and hormones |
| GNPAT | AR | rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata type 2 | enzyme in synthesis of ether phospholipids |
| PEX13 | AR | Zellweger syndrome | peroxisomal membrane protein |
| RAB3GAP1 | AR | Warburg micro syndrome | catalytic subunit of a Rab GTPase activating protein |
| LRP2 | AR | Donnai-Barrow syndrome | low density lipoprotein-related protein 2 |
| CYP27A1 | AR | cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis | member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily |
| KCNJ13 | AD | snowflake vitreoretinal degeneration | member of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel family |
| COL7A1 | AR | epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica | alpha chain of type VII collagen |
| FLNB | AD, AR | Larsen syndrome/spondylocarpotarsal synostosis syndrome | member of the filamin family |
| CNBP | AD | myotonic dystrophy type 2 | a nucleic-acid binding protein with 7 zinc-finger domains |
| SLC33A1 | AR | congenital cataracts, hearing loss, neurodegeneration | required for the formation of O-acetylated (Ac) gangliosides |
| HMX1 | AR | oculoauricular syndrome | transcription factor that belongs to the H6 family of homeobox proteins |
| CC2D2A | AR | Joubert syndrome 9 | play a critical role in cilia formation |
| SRD5A3 | AR | Kahirazi syndrome | steroid 5-alpha reductase family |
| ETFDH | AR | glutaric acidemia | component of the electron-transfer system in mitochondria |
| TRAPPC11 | AR | muscular dystrophy limb girdle 2S | a subunit of the TRAPP (transport protein particle) tethering complex |
| ERCC8 | AR | Cockayne syndrome type A | a WD repeat protein |
| VCAN | AD | Wagner syndrome 1 | a member of the aggrecan/versican proteoglycan family |
| SIL1 | AR | Marinesco-Sjögren syndrome | resident endoplasmic reticulum N-linked glycoprotein |
| TFAP2A | AD | branchiooculofacial syndrome | a transcription factor |
| GCM2 | AD | hypoparathyroidism familial isolated | a homolog of the Drosophila glial cells missing gene |
| NEU1 | AR | sialidosis type 2 | a lysosomal enzyme that cleaves terminal sialic acid residues |
| GJA1 | AD | oculodentodigital dysplasia | a member of the connexin gene family |
| PEX7 | AR | rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata type 1 | cytosolic receptor for the set of peroxisomal matrix enzymes |
| PEX3 | AR | Zellweger syndrome | involved in peroxisome biosynthesis and integrity |
| FAM126A | AR | hypomyelinating leukodystrophy 5 | part in the beta-catenin/Lef signaling pathway |
| PEX1 | AR | Zellweger syndrome | a member of the AAA ATPase family |
| CAV1 | AD | partial lipodystrophy, congenital cataracts, neurodegeneration syndrome | main component of the caveolae plasma membranes |
| AGK | AR | Sengers syndrome | a mitochondrial membrane protein involved in lipid and glycerolipid metabolism |
| ESCO2 | AR | Roberts syndrome | acetyltransferase activity may be required for the establishment of sister chromatid cohesion |
| EYA1 | AD | branchiootorenal syndrome 1 | a member of the eyes absent (EYA) family of proteins |
| PXMP3 | AR | Zellweger syndrome | an integral peroxisomal membrane protein required for peroxisome biogenesis |
| CNGB3 | AR | achromatopsia 3 | the beta subunit of a cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel |
| RECQL4 | AR | Rothmund Thompson syndrome | DNA helicase that belongs to the RecQ helicase family |
| GALT | AR | galatosemia | galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase |
| VLDLR | AR | cerebellar hypoplasia and mental retardation with or without quadrupedal locomotion 1 | low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| FKTN | AR | muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy | a putative transmembrane protein localized to the cis-Golgi compartment |
| LMX1B | AD | nail-patella syndrome | a member of LIM-homeodomain family of proteins |
| POMT1 | AR | muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy A1 | an O-mannosyltransferase |
| ERCC6 | AR | cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome I/Cockayne syndrome type B | a DNA-binding protein that is important in transcription-coupled excision repair |
| PTEN | AD | Cowden disease | a tumor suppressor |
| ALDH18A1 | AD/AR | cutis laxa AD/cutis laxa AR | a member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase family |
| OAT | AR | gyrate atrophy of choroid and retina | mitochondrial enzyme ornithine aminotransferase |
| PTH | AD/AR | familial isolated hypoparathyroidism | a member of the parathyroid family of proteins |
| LRP5 | AR, AD | exudative vitreoretinopathy 4/osteopetrosis, autosomal dominant 1 | a transmembrane low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| DHCR7 | AR | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome | an enzyme that removes the C(7–8) double bond in the B ring of sterols |
| CLPB | AR | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria with cataracts, neurologic involvement, neutropenia | member of the ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities (AAA+) superfamily |
| FZD4 | AD | retinopathy of prematurity | a member of the frizzled gene family |
| MMP1 | AR | epidermolysis bullosa dystrophic | a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases |
| CRYAB | AD | myofibrillar myopathy | members of the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family |
| SC5DL | AR | lathosterolosis | enzyme of cholesterol biosynthesis |
| JAM3 | AR | hemorrhagic destruction of brain, subependymal calcification | immunoglobulin superfamily gene member |
| TUBA1A | AD | lissencephaly | microtubule constituents of to the tubulin superfamily |
| PEX5 | AR | Zellweger syndrome | protein essential for the assembly of functional peroxisomes |
| MVK | AR | mevalonic aciduria | peroxisomal enzyme mevalonate kinase |
| GJB6 | AD | Clouston syndrome | one of the connexin proteins |
| B3GALTL | AR | Peters-plus syndrome | a beta-1,3-glucosyltransferase that transfers glucose to O-linked fucosylglycans on thrombospondin type-1 repeats |
| ITM2B | AD | cerebral amyloid angiopathy | a transmembrane protein |
| COL4A1 | AD | cerebral small vessel disease | a type IV collagen alpha protein |
| SEC23A | AR | craniolenticulosutural dysplasia | a member of the SEC23 subfamily of the SEC23/SEC24 family |
| POMT2 | AR | muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy | an O-mannosyltransferase |
| BUB1B | AR | mosaic variegated aneuploidy syndrome 1 | a kinase involved in spindle checkpoint function |
| FBN1 | AD | Weill-Marchesani syndrome | a member of the fibrillin family of proteins |
| POLG | AD/AR | progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions 1 | the catalytic subunit of mitochondrial DNA polymerase |
| GFER | AR? | progressive mitochondrial myopathy, sensorineural hearing loss, developmental delay | structural and functional homolog of the yeast scERV1 gene |
| NOD2 | AD | Blau syndrome | a member of the Nod1/Apaf-1 family |
| ADAMTS18 | AR | Knobloch syndrome | a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) protein family |
| MAF | AD | Aymé-Gripp syndrome | a DNA-binding, leucine zipper-containing transcription factor |
| YWHAE | AD | Miller-Dieker lissencephaly syndrome | member of the 14-3-3 family of proteins which mediate signal transduction by binding to phosphoserine-containing proteins |
| PEX12 | AR | Zellweger syndrome | member of the peroxin-12 family |
| WNT3 | AR | tetraamelia syndrome | secreted signaling proteins implicated in oncogenesis |
| XYLT2 | AR | spondyloocular syndrome | an isoform of xylosyltransferase, which belongs to a family of glycosyltransferases |
| EPG5 | AR | Vici syndrome (immunodeficiency, cleft lip/palate, cataract, hypopigmentation, absent corpus callosum) | a large coiled-coil domain-containing protein that functions in autophagy |
| CTDP1 | AR | congenital cataracts, facial dysmorphism, neuropathy | a protein which interacts with the carboxy-terminus of the RAP74 subunit of transcription initiation factor TFIIF |
| MAN2B1 | AR | alpha-mannosidosis | an enzyme that hydrolyzes terminal, nonreducing alpha-D-mannose residues in alpha-D-mannosides |
| DMPK | AD | myotonic dystrophy 1 | a serine-threonine kinase |
| FKRP | AR | muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy | a protein which is targeted to the medial Golgi apparatus and is necessary for posttranslational modification of dystroglycan |
| ABHD12 | AR | polyneuropathy, hearing loss, ataxia, retinitis pigmentosa, cataract | an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol |
| SALL4 | AD | Duane-radial ray syndrome | a zinc finger transcription factor thought to play a role in the development of abducens motor neurons |
| GNAS | AD | pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1A/pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1C/pseudohypoparathyroidism | multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms |
| COL18A1 | AR | Knobloch syndrome 1 | alpha chain of type XVIII collagen |
| PEX26 | AR | Zellweger syndrome | member of the peroxin-26 gene family |
| NF2 | AD | neurofibromatosis type 2 | a protein similar to ezrin, radixin, moesin family of proteins |
| LARGE | AR | muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy | a member of the N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase gene family |
| MYH9 | AD | Fechtner syndrome | a conventional non-muscle myosin |
| BCOR | XL | microphthalmia syncromic 2 | an interacting corepressor of BCL6 |
| PQBP1 | XL | Renpenning syndrome | a nuclear polyglutamine-binding protein that is involved with transcription activation |
| EBP | XL | chondrodysplasia punctata 2 | an integral membrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum |
| ARSE | XL | chondrodysplasia punctata 1 | a member of the sulfatase family |
| HCCS | XL | linear skin defects with multiple congenital anomalies | an enzyme that covalently links a heme group to the apoprotein of cytochrome c |
| AIC | XL | Aicardi syndrome | unknown |
| NHS | XL | Nance-Horan syndrome | a protein containing 4 conserved nuclear localization signals |
| GLA | XL | Fabry disease | a homodimeric glycoprotein that hydrolyzes the terminal alpha-galactosyl moieties from glycolipids and glycoproteins |
| COL4A5 | XL | Alport syndrome | one of the 6 subunits of type IV collagen |
| OCRL | XL | Lowe oculocerebrorenal syndrome | an inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase |
| IKBKG | XL | incontinentia pigmenti | regulatory subunit of the inhibitor of kappaB kinase complex |
AD, autosomal dominant; AR, autosomal recessive; XL, X linked.




CRYBB2, OCRL
More than 100 genes have been associated with cataracts. 35 genes associated with isolated cataracts and not syndromic.
Next Generation Sequencing / Wes
Some physicians believe when only cataracts, due to high cost, investigation isn’t warranted.
All 3 types of inheritance present, but autosomal dominant is the most frequent. Accounting for 75% of all hereditary cataracts (Book). Can vary among family members and some may not know that they have them
Crystallins are major protein components of the lens and are crucial to maintaining lens transparency. Mutations in crystallin genes represent a large portion of autosomal dominant cataracts. Including CRYAA, CRYBB, CRYAB, CRYGC, and CRYGD. Most cataracts are inherited in autosomal dominant fashion- but some are not